Thoughts on Lead Acid Battery Maintenance
Created: December 7, 2010
Last Revised: October 23, 2023
French Creek Valley Home
My Blacksmthing Page
Vehicle Maintenance
Contact Us
Introduction
I maintain more than 26 lead acid batteries. Some are in automobiles and vans that are used on a regular basis and some are in
vehicles and machines used
seasonally, while others are used as low voltage power supplies for various projects.
22 of them are in what I call the "seasonal" vehicles. The only thing I do for the 4 "regular use" vehicle
batteries is to periodically check the terminal voltages
after the vehicles have been at rest for 24 hours to verify that the charging system is working and that the battery is
fully charged(see Battery Charge Level Chart, below).
For maintenance purposes I have several of the $7 (on sale) HF maintenance chargers, a 500 Amp Harbor Freight Battery Load Tester,
a digital VOM---

---and a log that lists all the batteries, by the name of the vehicle that they are in.
Maybe I am a data freak but I made an Excel spreadsheet of my "log".
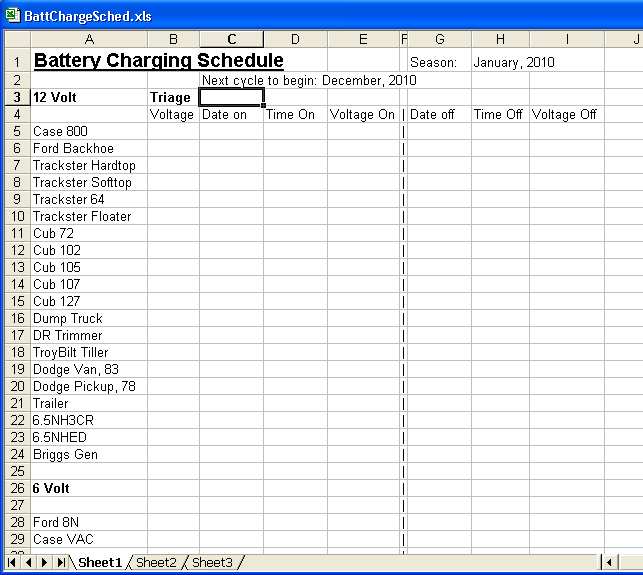
Each season, I simply print a copy, put it on a
clip board, and go about my battery maintenance job.
My Battery Maintenance Process
In about December, up here in central Wisconsin, I check each "Seasonal" battery's voltage with a digital vom and recharge
the worst four first, recording the event(date, time and voltage) on my log.
If this "trieage" voltage is less than about 12.2, I consider replacing that battery next spring.
-Don't worry about sitting lead-acid batteries on a concrete floor. I'd like to see any significant data (not a single
anecdote or an old mechanics tale) to show that's a problem. Lower temp is better to slow chemical reactions.
Actually, the concrete floor would probably keep the battery warmer than if it were in ambient air in an unheated space.
-There's no point in disconnecting the batteries from my old vehicles, but I would do that if I had any vehicles that were new
enough to be drawing a trickle of current all the time.
-I recharge about 4 batteries at a time with 4 of the above mentioned chargers. The batteries stay on the charger for about
3 days to one week.
Then I remove the chargers, record the charger-removal event and move on to the next 4.
With good batteries, they almost all have a terminal voltage between 13.04 and 13.07 as soon as I remove the charger.
Much lower than that suggests a looming problem, But--- One day later I check the voltage of the last 4 I charged and
record that. That's the voltage they will stabilize at for some period of time. One can see from this value what the
battery is capable of doing and about how long it will be before it will need replacement.
I repeat this whole thing again in about late March.
Notes
The best way to make batteries last a long time is to:
1: Make sure the vehicle's charging circuit is working properly
2: Make sure the starting system and engine are well tuned up so the battery never
gets discharged deeply in the starting process.
3: If a battery DOES get discharged deeply for some reason, such as leaving the trunk
open or the lights on, recharge it immediately.
4: As I put this page together, I noticed that I didn't mention the use of a battery hydrometer even once.
"Why not?", I asked myself. Well, for most batteries out there today, it's a big deal to even get into the cells to add
water, leave alone to take a specific gravity reading.
Also, the use of the Battery Charge Level Chart, below, pretty much takes the place of measuring specific gravity for me.
If I had batteries that were constantly being drawn down a lot, as in a wind or solar pv application, I sure would use the
hydrometer a lot.
Battery Charge Level Chart (Let the battery sit for 24 hours after charging before measuring):
Voltage Percent of Full charge
---------- ----------------------------
12.7 100%
12.4 75%
12.2 50%
12.0 25%
------------------------------------------------------------------
Using a Battery Load Tester
The table above is usually a good indicator of battery condition, but not always.
Now and then, a battery will show a decent
voltage, but when you try to use it to start its vehicle, it dies on the first few turns. To avoid being surprised in this
way, I recently bought a Harbor Freight 500 amp Battery Load Tester. To use it, you connect it to the battery to be tested
and,using the big knob on the tester, crank the current up to 1/2 the cold cranking amps listed on the battery. Then wait
for a built-in timer to beep, and read the good/questionable/bad voltage scale to estimate the battery's actual capability.
A useful tool if you have enough batteries to make it worth while.
Harbor Freight's 500 amp model is what I need for most of my batteries, but I do still have 2 tractors with 6
volt batteries, which this tester won't handle. HF does sell a 100 amp model that works for both 6 and 12 volts, but 100
amps isn't enough of a test for any of my "car size" batteries, so was of no real value to me. I suppose that if a person
had only garden tractor or motorcycle batteries to test, then the 100 amp model would be an okay investment.

